Can Grooved Elbows Handle High-Pressure Steam?
Grooved elbows can, without a doubt, handle high-pressure steam, but their appropriateness depends on a few vital components. These fittings are outlined to withstand critical weight and temperature variations, making them reasonable alternatives for steam conveyance systems. In any case, the particular weight rating, fabric composition, and fabricating quality of the grooved elbow fitting play significant parts in deciding its execution under high-pressure steam conditions. It's basic to select grooved elbows that are unequivocally evaluated for steam applications and meet the required weight and temperature requirements of your system. Legitimate establishment, normal upkeep, and adherence to industry measures are too basic for guaranteeing the secure and productive operation of grooved elbows in high-pressure steam environments.
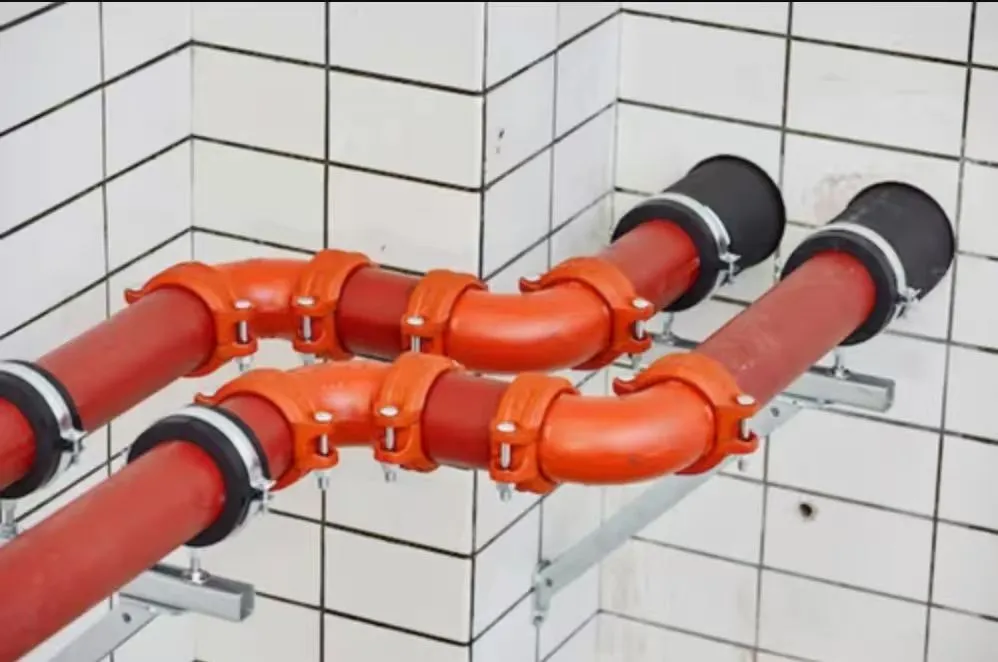
Design and Strength Characteristics of Grooved Fittings Under Pressure
Engineering Principles Behind Grooved Elbow Design
Grooved elbows are designed with exactness to withstand the demanding conditions of pressurized frameworks. The plan consolidates a few key highlights that contribute to their quality and unwavering quality. The grooved ends of these fittings are machined to demanding resistances, guaranteeing a secure connection when coupled with suitable grooved pipe fragments. This accurate machining permits uniform stretch dissemination over the fitting, minimizing weak points that seem to lead to disappointment under high pressure.
The body of a grooved elbow is ordinarily thicker than standard pipe dividers, giving extra basic astuteness. This expanded divider thickness is especially pivotal in ranges where the stream changes course, as these focuses involve higher push concentrations. Computer-aided design (CAD) and limited component examination (FEA) procedures are utilized to optimize the elbow's geometry, guaranteeing it can withstand the forces applied by high-pressure steam without compromising its integrity.
Material Selection for High-Pressure Applications
The choice of fabric for grooved elbows for high-pressure steam applications is vital. Pliable press and carbon steel are common materials utilized due to their amazing strength-to-weight ratios and capacity to withstand high temperatures. These materials are carefully chosen for their resistance to crawl, a phenomenon where materials gradually distort beneath consistent push, which is especially pertinent in high-temperature steam environments.
For more requesting applications, specialized alloys such as chrome-molybdenum steel or austenitic stainless steel may be utilized. These materials offer prevalent erosion resistance and maintain their quality at raised temperatures, making them perfect for high-pressure steam frameworks. The choice of fabric also takes into account variables such as warm development, weakness resistance, and compatibility with the steam medium to guarantee long-term reliability.
Reinforcement Techniques for Enhanced Pressure Resistance
To assist in supporting the pressure-handling capabilities of grooved elbows, different support strategies may be actualized. One such strategy is the utilization of fortifying rings or collars around basic zones of the fitting. These extra components offer assistance to distribute stretch more equitably and give additional support where it's most needed.
Another approach includes the key thickening of certain areas of the elbow, especially at the points where the direction of the stream changes. This particular fortification addresses the zones most vulnerable to stretch concentration without unnecessarily expanding the by and large weight of the fitting. A few producers, moreover, utilize progressed warm treatment forms to upgrade the material's microstructure, resulting in progressed quality and toughness under high-pressure conditions.
Temperature Limits and Pressure Ratings for Steam Distribution Systems
Understanding Pressure-Temperature Connections in Steam Systems
The relationship between weight and temperature in steam frameworks is perplexing and follows well-established thermodynamic standards. As the weight increments, so does the immersion temperature of steam, which is the temperature at which water bubbles at a given weight. This relationship is basic when planning and selecting components for steam conveyance frameworks, including grooved elbows.
Engineers must consider the whole working extent of the framework, from startup to full-stack conditions. The pressure-temperature bend for steam is non-linear, meaning that little changes in weight can result in critical temperature variations, particularly at higher weights. This non-linearity requires cautious thought when indicating grooved elbows and other fittings to guarantee they can withstand both the greatest weight and the corresponding temperature.
Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP) for Grooved Fittings
The Most Extreme Admissible Working Weight (MAWP) is a vital detail for grooved elbow fittings in steam applications. This esteem speaks to the most elevated weight at which the fitting can securely work beneath ordinary conditions. MAWP is decided through thorough testing and investigation, taking into account variables such as fabric properties, plan geometry, and security margins.
For high-pressure steam frameworks, grooved elbows may have MAWP evaluations extending from 300 psi to over 1000 psi, depending on their design, material, and plan. It's imperative to note that the MAWP is regularly indicated at a reference temperature, frequently 100°F (38°C). As temperatures increase, the passable working weight may need to be derated to account for the diminishment in fabric quality at lifted temperatures.
Temperature Limitations and Their Impact on Fitting Performance
Temperature plays a noteworthy part in the execution and life span of grooved elbows in steam systems. As temperatures rise, materials can involvement changes in their mechanical properties, including decreased ductility and increased vulnerability to creep. These changes can influence the fitting's capacity to keep up a secure seal and withstand framework weights over time.
Most grooved elbows outlined for steam applications have temperature evaluations that expand up to 366°F (186°C) or higher, depending on the fabric and plan. Past these temperatures, extraordinarily high-temperature amalgams or elective fitting sorts may be essential. It's pivotal to consider not as it were the steady-state working temperature but also potential temperature spikes amid framework startup or disturbed conditions when selecting grooved elbows for high-pressure steam service.
Testing Standards and Safety Compliance for High-Pressure Applications
Industry Benchmarks Overseeing Grooved Fitting Performance
Grooved elbows expecting high-pressure steam applications must follow exacting industry benchmarks to guarantee their security and unwavering quality. Organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) have created comprehensive rules for the planning, fabrication, and testing of pressure-containing components.
ASME B31.1 Control Channeling Code is especially significant for steam frameworks, giving requirements for channeling ordinarily found in electric control creating stations, mechanical and regulation plants, and central heating systems. This standard diagrams the vital plan considerations, design determinations, and creation strategies for components like grooved elbows working beneath tall weight and temperature conditions.
Rigorous Testing Protocols for Pressure-Bearing Components
To confirm the execution of grooved elbow fittings in high-pressure steam situations, producers utilize a battery of tests. Hydrostatic testing is a common strategy where the fitting is subjected to weights altogether higher than its evaluated working weight to guarantee its basic integrity. This test regularly includes pressurizing the elbow to 1.5 times its maximum admissible working pressure and holding it for an indicated term to check for spills or deformation.
Burst testing is another basic assessment where the elbow is pressurized until failure occurs. This damaging test gives important information on the extreme quality of the fitting and makes a significant difference in approved plan calculations. Also, cyclic weight testing may be conducted to reenact the impacts of weight changes over time, surveying the elbow's weariness resistance and long-term reliability.
Certification and Quality Assurance Measures
Ensuring the security and unwavering quality of grooved elbows for high-pressure steam applications includes thorough quality affirmation forms and third-party certifications. Producers frequently look for certifications from recognized bodies such as Financiers Research facilities (UL) or FM Endorsements to illustrate compliance with industry benchmarks and execution requirements.
Quality confirmation measures ordinarily incorporate fabric traceability, dimensional reviews, and non-destructive testing strategies like radiography or ultrasonic review to identify any internal imperfections. Numerous producers moreover execute factual control methods to screen and maintain steady product quality throughout the production process. These comprehensive quality affirmation programs offer assistance to guarantee that each grooved elbow clearing the production line meets the demanding benchmarks required for secure operation in high-pressure steam systems.
Conclusion
Grooved elbows can without a doubt handle high-pressure steam when legitimately planned, made, and introduced. Their capacity to withstand demanding conditions stems from progressive design standards, careful material selection, and thorough testing procedures. Be that as it may, it's significant to select fittings particularly evaluated for steam applications and adhere to industry measures and best practices. By considering components such as pressure-temperature connections, greatest passable working weight, and temperature confinements, engineers can certainly join grooved elbows into high-pressure steam frameworks, guaranteeing security, productivity, and long-term reliability.
FAQs
What materials are commonly utilized for grooved elbows in high-pressure steam applications?
Ductile press and carbon steel are often as possible utilized, with specialized alloys like chrome-molybdenum steel for more demanding conditions.
How do grooved elbows compare to welded fittings for steam systems?
Grooved elbows offer less demanding establishment and support, whereas welded fittings may give higher weight appraisals in a few cases.
What is the common weight extension for grooved elbows in steam systems?
Depending on the estimate and plan, grooved elbows can handle weights from 300 psi to over 1000 psi in steam applications.
Expert Grooved Elbow Solutions for High-Pressure Steam Systems | FLA Industrial
At FLA Mechanical &; Exchanging Co., Ltd., we specialize in giving top-quality grooved elbows designed to exceed expectations in high-pressure steam situations. Our broad involvement in fabricating equipment, instruments, and pipe fittings guarantees that our items meet the most rigorous industry standards. With our progressive innovation and strict quality administration, we provide solid, high-performance grooved elbow fittings that can withstand the challenges of demanding steam applications. For master direction on selecting the right grooved elbows for your high-pressure steam framework, contact our group at sales@flaindustrial.com.
References
ASME B31.1-2020 Power Piping Code. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020.
Spirax Sarco. "Steam and Condensate Loop Book." 2021 Edition.
Mohitpour, M., et al. "Pipeline Design & Construction: A Practical Approach." ASME Press, 2018.
Nayyar, M.L "Piping Handbook." 8th Edition, McGraw-Hill Education, 2017.
Antaki, G.A. "Piping and Pipeline Engineering: Design, Construction, Maintenance, Integrity, and Repair." CRC Press, 2019.
Becht, C. "Process Piping: The Complete Guide to ASME B31.3." ASME Press, 2018.
Send your inquiry now and start your cooperation with our experienced team.